Deploying the Web Application¶
Setup¶
This section pertains to the setup of the Django web application using Elastic Beanstalk and a Linux operating system. A more general guide (including setup using Windows) can be found in AWS documentation.
This guide was made using Python version 2.7.10. After downloading the DustyDjango code from `here`_. Navigate to terminal, and install the virtualenv package using:
pip install virtualenv
virtualenv is a tool to create isolated Python environments. More information about the package can be found here.
Next we create a new virtualenv called atamo via:
source virtualenv ~/atamo
To activate the virtualenv, run:
source atamo/bin/activate
You will see (atamo) prepended to your command prompt, indicating that you’re in a virtual environment. Install the required version of django using:
(atamo)~$ pip install django==1.10.8
Verify installation of packages at any time using pip freeze, which now should display:
(atamo)~$ pip freeze
Django==1.10.8
Change directories into the project application (downloaded previously - DustyDjango). In this example the directory where the project is currently stored is called atamoapp_demo. To change directory, use:
(atamo)~$ cd atamoapp_demo
Your directory (here called atamoapp_demo) should have now have a layout similar to:
atamoapp_demo/
├ manage.py
├ .db.sqlite3
├ [DIR] mysite
├ [DIR] blog
The following dependencies are needed for the proper functioning of the application. Verify the following packages are installed using pip freeze. If the following packages are not installed, install them using ``pip install `` followed by the desired package and version number download.
pip freeze
boto3==1.4.7
botocore==1.7.33
certifi==2017.7.27.1
chardet==3.0.4
decorator==4.1.2
Django==1.10.8
django-allauth==0.33.0
docutils==0.14
enum34==1.1.6
functools32==3.2.3.post2
futures==3.1.1
idna==2.6
ipython-genutils==0.2.0
jmespath==0.9.3
jsonschema==2.6.0
jupyter-core==4.3.0
nbformat==4.4.0
oauthlib==2.0.4
plotly==2.1.0
python-dateutil==2.6.1
python-openid==2.2.5
pytz==2017.2
requests==2.18.4
requests-oauthlib==0.8.0
s3transfer==0.1.11
six==1.11.0
traitlets==4.3.2
urllib3==1.22
Deployment¶
This section pertains to the deployment of the Django web application using Elastic Beanstalk and a Linux operating system. A more general guide (including setup using Windows) can be found in AWS documentation.
After following the above set-up has been complete, you are now ready to deploy via Elastic Beanstalk. To do so, you will first need to ensure you have Git installed on your machine.
Activate your previously created virtualenv using:
source atamo/bin/activate
Change to your project directory:
(atamo)~$ cd atamoapp_demo
If this is your first time deploying an application via Elastic Beanstalk, first download the command line interface. As in this example we are connecting to an existing app, the deployment instructions differ from a fresh deployment. Please see Elastic Beanstalk documentation if you wish to deploy a _brand new_ application.
Next run:
(atamo)~$ eb init -i
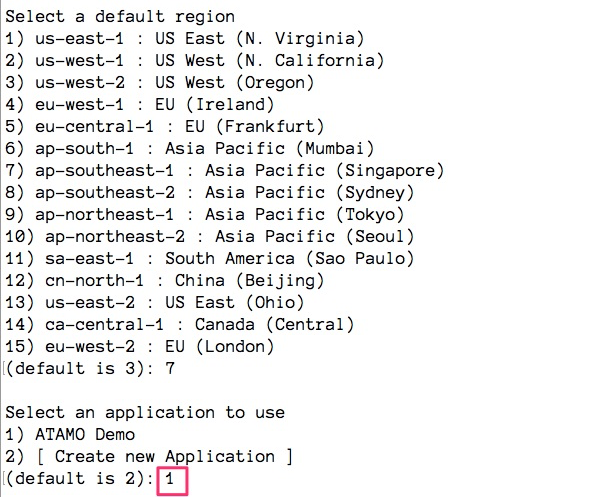
Which will prompt you to select a default region. Type the number 7 (which corresponds to ap-southeast-1). It will then prompt you to select an application: Choose ATAMO Demo.
Once you’ve successfully established the connection, you just need to commit your changes to Git.
(atamo)~$ git init
(atamo)~$ git add .
(atamo)~$ git commit -m “First commit”
Where “First commit” is any commit message that you desire. Please ensure you include an appropriate .gitignore file for any additional files you do not wish to deploy live. Finally, run:
(atamo)~$ eb deploy
Which will deploy your application. If you are not automatically redirected to the URL, use:
(atamo)~$ eb open